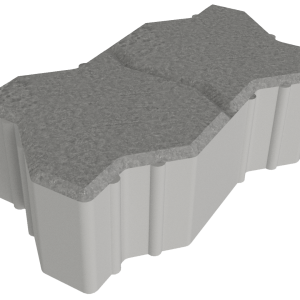
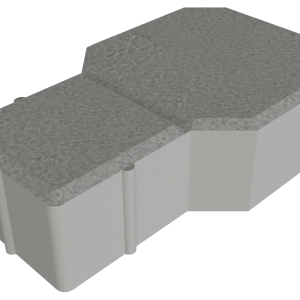
Concobble
Concobble, an innovative and exclusive paver. A modern replica of cobble stone.
Available in square and wedge shapes and in a variety of colours.
| Thickness Available | Length Width | Block mass p/m² | No. blocks p/m² |
| WEDGE: | |||
| 55mm | 116×112/67 | 12.1kg | 92 |
| 60mm (on request only) | 116×112/67 | 12.1kg | 92 |
| SQUARE: | |||
| 55mm | 116×116 | 12.1kg | 74 |
| 60mm (on request only) | 116×116 | 12.1kg | 74 |
Colours Available: Grey, Slate, Terracotta, Plum, Tan, Autumn
General Application: Domestic driveways, municipal parking areas, pedestrian pavements, pathways & commercial developments.
What is paving:
Pavement, in construction, is an outdoor floor or superficial surface covering.
Paving materials include asphalt, concrete, stones such as flagstone, cobblestone, and setts, artificial stone, bricks, tiles, and sometimes wood.
In landscape architecture, pavements are part of the hardscape and are used on sidewalks, road surfaces, patios, courtyards, etc.
Pavement laid in patterns like mosaics were commonly used by the Romans.
Stone is a worthwhile addition inside and outside of the home.
From a striking exterior cobble walkway to a timeless interior clad stone wall – stone is classic!
We have some stunning new additions to our product range – perfect for any home renovation or project!
Critical considerations when doing you’re paving:
- Step 1 – Choosing the right paver:
- There are a number of pavers available for various applications.
- Flagstones are generally wet cast pavers that can be moulded into a number of shapes, ideal for gardens, patios and pool surrounds.
- Clay bricks like Corobrick are generally used for driveways, walkways and pool surrounds, although, in our opinion, this is somewhat out of fashion.
- Step 2 – Ground preparation
- Ground preparation is important as any sort of unprepared ground can result in ‘pooling’, sagging paving and loose bricks.
- Step 3 – Laying the base materials
- Depending on what paver you’re laying, it will determine what base material you’ll use.
- Flagstones will need a bed of cement about 10cm thick to rest on, while other paving will need a bed of river sand, about 20cm, to rest on.
- Step 4 – Laying the paving
- Once the base material has been laid and screeded with a long plank, (take care not to compact the base material) start laying your paving.
- There are a number of patterns to choose from, including stretcher bond, herring bone, basket weave and so on.
- Step 5 – Grouting
- Once all the paving has been laid, you’re ready to grout. Once that’s done, you can enjoy the fruits of your labour.
- Step 6 – Enjoy the fruits of your labour
- For a small job, the above guide should be more than enough to ensure a happy result.
- If you’re working with a larger area, get a professional to tackle it.
Visit us on Facebook
Or Contact us.















Reviews
There are no reviews yet.